Skin manifestations of diabetes: itching and dry skin. Skin manifestations of diabetes mellitus - may be the first symptoms of the disease Skin diseases of type 2 diabetes
Diabetic dermopathy often becomes one of the signs of the development of diabetes mellitus. As a result of insufficient insulin production, skin problems arise in diabetes mellitus, and almost all metabolic processes in the body are disrupted - carbohydrate, fat, protein.
In diabetes mellitus, the skin changes its structure and darkening of the skin is observed.
Approximately ninety percent of people with diabetes have various skin problems. Under normal conditions, the skin has a high level of elasticity, which is achieved due to the necessary water content in the body's cells.
As a result of impaired water metabolism and rapid dehydration, skin tissue in type 2 diabetes loses its elasticity and becomes rough and rough. What does skin look like with diabetes mellitus? Photos of such disorders can be easily found in specialized literature.
What changes occur in the body?
Almost all systems and organs are exposed to pathological changes that occur throughout the body as a result of the development of diabetes mellitus. Skin diseases are just one of many problems that arise.
The main causes of skin damage in diabetes mellitus are the influence of the following factors:
- ongoing metabolic disturbances;
- accumulation of abnormal metabolic products in tissues and cells;
- development of skin disorders in diabetes;
- decreased body immunity;
- the appearance of inflammatory processes in the follicles, epidermis and sweat glands from diabetes.
As a result of the influence of all of the above factors, the skin becomes infected with various pathogenic microorganisms. The photo shows what the skin looks like with diabetes.
Gradual changes in diabetic skin can be observed as the disease progresses. After a certain period of time, constant itching and profuse peeling of the epidermis begins to appear, which can “fall off” in whole plates. If this process develops on the scalp, the constantly accompanying symptoms begin.
Various sized spots or severe rashes may appear on different parts of the body and face, which constantly itch and cause discomfort. In addition, the nail plates on the hands and feet undergo significant changes. They lose their original shape, become extremely thick and acquire a yellowish tint.
In addition, areas of the body that are susceptible to constant friction, such as the palms and feet, can also cause a feeling of discomfort. First of all, there is a pronounced keratinization, the appearance of calluses and a change in normal color to yellow.
The main changes that occur to the skin during the development of the disease are as follows:
- dry and rough skin that is constantly thinning;
- nail plates grow;
- there is a gradual callus on the palms and soles of the legs;
- the skin may acquire an unnatural yellow tint.
 Today, there are three main groups of skin diseases that appear as a result of diabetes.
Today, there are three main groups of skin diseases that appear as a result of diabetes.
Primary pathological processes on the skin that arise as a result of changes occurring in blood vessels and metabolic disorders;
Secondary pathological processes, which are various infectious diseases, and arise as a result of a general decrease in immunity and the vital activity of various fungi and bacteria;
Skin diseases in diabetes, which occur in the form of allergic reactions in response to taking various medications.
What skin diseases most often develop?
Sugar level
Skin lesions can manifest themselves in the form of a variety of rashes, plaques and blisters, which are influenced by various external and internal factors. Such diseases include:
- Diabetic pemphigus. Its manifestation is very similar to sunburn and often affects the area of the shoulders, arms, and legs. Such a bubble or blister does not cause painful discomfort and, as a rule, disappears quickly.
- Various rashes that are allergic in nature and appear as a result of the use of a large number of different medications, insect bites or food.
- Granuloma annulare appears as red or brown rashes on the skin. In some cases, granuloma is treated with steroids.
In addition, skin diseases in diabetes, which belong to the primary group, can appear in the form of:
- If the disease is accompanied by the development of atherosclerosis, dry skin may occur, it becomes thinner and becomes pale. In addition, due to disruption of normal blood flow, problems with the healing of even the smallest wounds and the appearance of infectious ulcers are observed.
- hypodystrophy of the diabetic type. With the development of this disease, redness and thinning of the skin are observed. Accompanying symptoms may include itching, burning and pain in the affected areas.
- Diabetic dermatopathy is one of the most common skin diseases. As a rule, it affects the front areas of the lower leg in the form of small red-brown spots. Over time, such redness disappears and becomes a bright brown hue, while the area and structure of the spot changes.
- Diabetic scleroderma. Basically, during the course of the disease, a finger or hand is damaged, the skin tightens, and problems arise with the flexibility of the joints.
Various infectious skin lesions in diabetes are especially dangerous, since wounds heal poorly. Fungi and bacteria entering such areas begin their negative impact. Often, as a result of their vital activity, wet ulcers can occur.
Regardless of what changes occur to the skin, proper treatment must be started immediately. In some cases, it is enough to simply monitor sugar levels, diet, and adherence to all hygiene rules more carefully.
The condition of the skin directly depends on the development of diabetes, which is why if you follow all the recommendations of your doctor, you can achieve significant improvements.
How are diseases treated?
Spots, darkening and other skin inflammations can occur in patients of any age (including children). One of the most important components of therapy is strict adherence to the diet. It is nutrition that will improve not only the condition of the skin, but also the general well-being of the patient.
The attending physician may recommend purchasing the necessary medicinal ointments that have an antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effect. In addition, it is necessary to regularly smear your hands and other parts of the body with special vegetable oils or creams to soften dead skin.
If any spots appear or the skin begins to darken, you need to seek help from a medical specialist, because only your doctor can help you choose the right care.
Treatment also aims to provide ongoing protection from hot sun rays, strong winds or cold. Protective products must be regularly applied to the skin to protect against burns, chapping or hypothermia.
It is believed that the drug Dimexide has excellent antifungal and antimicrobial effects. It is perfect for the development of any inflammatory processes on the skin. Such diseases include furunculosis, purulent wounds, burns, thrombophlebitis and ulcers. That is why doctors often recommend using Dimexide if you have skin problems with diabetes. This drug promotes rapid healing of wounds and increases the body's resistance to low temperatures or radioactive radiation. In addition, Dimexide is one of the budget and affordable medicines.
In general, treatment of emerging candidiasis should include the following specific measures.
Antimycotic creams or ointments are used. The course of therapy is approximately five to seven days until the rash disappears completely.
If the disease affects large areas of the body, special solutions of anil dyes (can be water or alcohol based) are used.
Medications that have a good antifungal effect are used. These are, first of all, Fluconazole and Ketoconazole.
These products are affordable, but at the same time highly effective.
Preventive measures and traditional medicine recipes
Before treating skin problems, it is necessary to try to normalize all metabolic processes occurring in the body. The development or elimination of skin diseases will depend on the general improvement of the patient’s condition.
It should be noted that one of the most important aspects in complex therapy is proper nutrition. This issue must be taken seriously, strictly adhering to the prescribed diet. Sometimes incorrect measurement of the amount of food can lead to sudden jumps in sugar, which, in turn, negatively affect the general condition of the patient.
- the use of personal hygiene products without fragrances and with the required Ph level, which do not dry out the skin and do not cause irritation or allergic reactions;
- Regularly monitor rough skin on your feet using special products;
- The skin of the feet, especially the areas between the toes, requires gentle and careful care. This is where multiple bacteria and fungi can multiply.
- do not self-medicate calluses, cracks and other skin problems;
- carefully observe personal hygiene;
- in clothing, give preference to things made from natural fabrics that do not squeeze or rub the skin;
- if there are wounds, it is necessary to immediately disinfect them, but do not cover them with a medical plaster;
- If a rash or other skin problems appear, consult a doctor promptly.
- do not hot baths with the addition of oak or string bark;
- wipe the inflamed areas with a medicinal decoction prepared from birch buds;
- If you have rashes or other inflammations, you can wipe your skin with freshly cut aloe juice.
If itching of the skin occurs, you can prepare a medicinal decoction for external use to relieve the symptom. To do this, you need to take dry peppermint leaves, St. John's wort and oak bark. Pour three tablespoons of the mixture into a glass of boiling water and leave to steep for a while. Wipe the affected areas of the skin with warm infusion. The video in this article will show you what to do with your feet if you have diabetes.
The skin is one of the first organs to react to changes in carbohydrate metabolism. Due to a decrease in local immunity and the accumulation of metabolic products in the skin, the risk of developing various diseases increases. Most skin diseases manifest as rashes.
The skin is one of the first to react to a persistent increase in glucose in the circulating blood or hyperglycemia. Impaired carbohydrate metabolism leads to the appearance and accumulation of atypical metabolic products that disrupt the activity of the sweat and sebaceous glands. Changes in small vessels of the skin, polyangiopathy and disorders of the nervous regulation of vascular tone are combined in diabetes mellitus with problems of the immune system, both general and local. All these factors lead to various skin diseases, itching, scratching and infection.
Skin changes
The photo shows the state of the epidermis in diabetes mellitus. Normal skin has high turgor - elasticity. This is ensured by the normal water content in the cells. In diabetics, due to the fact that fluid is not retained in the body and is excreted through sweat and urine at an increased rate, the skin tissue loses its elasticity, becomes dry and rough, and this is felt when touched.
As the disease progresses, changes become more pronounced. Persistent skin itching and persistent, profuse peeling appear. The epidermis becomes thinner, peels off in entire plates, this is clearly shown in the photo. It is especially noticeable on the scalp, where flaking and itching are accompanied by increased hair loss, dullness, and dryness.

On the rest of the skin, spots of various sizes, colors, and rashes may appear, which may be accompanied by severe itching. The areas of the skin that are subject to friction - the sole and palms - become calloused, the skin becomes rough and may acquire a persistent yellow color. Any minor wound becomes problematic and does not heal for a long time.
A characteristic combination in diabetes mellitus is thinning of the skin with simultaneous hyperkeratosis (thickening) of the nail plates. Nails become several times thicker, turn yellow, change their shape - become deformed. Exactly how it looks is shown in the photo.

So, we can say that with diabetes, the skin undergoes the following changes:
- becomes dry, rough;
- becomes thinner;
- nail hyperkeratosis develops - the growth of nail plates;
- areas of calluses appear on the soles and palms;
- yellowing of the skin is observed.
However, all these problems become persistent over time. There are the most characteristic skin manifestations by which one can suspect or observe the effectiveness of treatment for diabetes.
Skin diseases in diabetes
One of the warning signs of diabetes mellitus is skin itching. It becomes persistent and causes the patient significant difficulties and inconvenience in everyday life. The patient scratches the itchy areas: the front surface of the leg, the groin area, thereby causing multiple damage to the epidermis (see photo). Such microcracks and scratches are difficult to treat, often become infected, and take a chronic course.
All skin diseases that appear in diabetes mellitus can be divided into several large groups.
- Associated with changes in blood vessels, metabolic disorders. These are the so-called primary skin diseases in diabetes.
- Skin infections: fungal and bacterial, which occur as secondary complications of damage to the epidermis.
- All other diseases that are provoked by therapeutic drugs and procedures during the treatment of the underlying disease.
Primary diseases
Dermatopathy

This includes diabetic dermatopathy. It occurs very often in diabetes. Spots appear on the front surfaces of the shins. They are colored intensely red-brown, significantly different from the rest of the skin. The spots have a clearly defined border, the color becomes steadily brown over time and the duration of the disease, and the structure of the affected area of the skin also changes.
This is due to changes in blood vessels in this area (shown in the photo). No special treatment is applied in this case. The condition is corrected by constantly maintaining sugar levels within normal limits.
Necrobiosis lipoidica
It is rare compared to other dermatoses in diabetes. The severity or progression of the rash does not depend directly on blood sugar levels. It occurs more often in people suffering from type 1 diabetes, which is insulin-dependent.

It is characterized by the appearance of pinkish spots that are not elevated above the rest of the skin level and have an elongated or rounded shape. In the center the spots are slightly sunken, closer to the edge they are raised, this is shown in the photo. Gradually, the central part of the spot atrophies, turns brown, and an ulcerative lesion may form.
These rashes are located on the front of the lower leg. There are no subjective painful sensations (itching, pain, peeling) until ulcerative changes form.
Treatment is based on drugs that normalize lipid metabolism (this includes, for example, Lipostabil) and drugs that normalize and improve microcirculatory processes of the skin (Trental, Curantil).
Treatment is indicated with the administration of corticosteroid drugs directly to the site of the lesion, compresses and application dressings with Dimexide solution. With the active development of ulcerative changes, surgical treatment using laser technology is possible.
Itching of the skin in diabetes mellitus is the most characteristic, or as it is also called, a warning sign. A characteristic feature of this symptom is the lack of direct correlation with blood glucose levels and the intensity of itching and rashes. On the contrary, as diabetes develops, the relevance of itching fades into the background; patients note its greatest intensity at the onset of the disease.
Secondary complications
Active scratching, persistent trauma to the skin with a simultaneous decrease in immunity, both general and local, sooner or later leads to the fact that minor lesions and wounds on the skin become infected with various microorganisms. Most often these are pathogens of fungal diseases. The fact is that it is fungal microorganisms that actively multiply under conditions of a shift in the pH of human skin during diabetes. Ideal conditions are created for them:
- violation of the pH of the skin;
- proliferation of epithelial plates - peeling, hyperkeratosis;
- excessive sweating leads to maceration - abrasions and diaper rash of the skin.
Fungal diseases in diabetes mellitus increase skin itching, are difficult to treat, leave behind spots of persistent pigmentation, rashes tend to grow and merge with each other, the photo shows skin candidiasis.

Treatment involves local treatment with antifungal ointments, aniline dyes (diamond green, Castellani). In some cases, the doctor prescribes antifungal drugs to be taken orally.
Infected skin rashes are much more common in people with diabetes than in people who do not have the disease. Itching leads to infection and serious complications. These include erysipelas, cellulitis, boils, carbuncles, paronychia and panaritium.
Conclusion
Successful treatment of skin diseases in patients with diabetes directly depends on the success of therapy for the underlying disease, the patient’s discipline in following recommendations for correcting blood sugar and monitoring its level. Without these conditions, effective treatment of skin rashes and diseases in diabetics is very difficult.
Diabetes mellitus is a very common disease caused by a lack of insulin in the blood and shows itself to disrupt many metabolic processes in the body. In particular, the skin that suffers first in diabetes mellitus is dermatitis and dermatoses, itching and dryness.
Clinical picture
What doctors say about diabetes
Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Aronova S. M.
I have been studying the problem of DIABETES for many years. It's scary when so many people die and even more become disabled due to diabetes.
I hasten to report good news - the Endocrinological Research Center of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences managed to develop a medicine that completely cures diabetes mellitus. At the moment, the effectiveness of this drug is approaching 100%.
Another good news: the Ministry of Health has achieved the adoption special program, which reimburses the entire cost of the drug. In Russia and the CIS countries, diabetics to can get the remedy FOR FREE.
Find out more>>
Reasons for the development of pathological changes

The reason that provokes the appearance of skin problems in diabetes mellitus in the form of itching and burning, redness and rashes, the formation of ulcers is a failure in carbohydrate metabolism. In this case, diabetes mellitus will show symptoms on the skin in the form of itching, especially in the genital area, long-lasting wounds and ulcerative tumors, and the appearance of excessive pigmentation.
Thus, skin lesions in type 2 diabetes show themselves much earlier than symptoms such as dry mouth and thirst, and frequent urge to go to the toilet. If you suspect the development of diabetes mellitus, or if you have problems with the dermis, you should visit a doctor and get tested.

So how does diabetes manifest itself on the skin? Initially, diabetic blisters gradually begin to appear on it. The latter can appear throughout the body, and not in a single area - along the back and chest, forearm and legs, especially under the armpits and under the chest, on the inside of the thigh.
The skin on the affected areas looks like after a burn - blisters and blisters do not cause much pain, other than cosmetic discomfort and do not require special medical treatment.
Today, complications of diabetes mellitus, which manifest themselves as rashes, itching and redness, can be divided into 3 groups.
Be careful
According to WHO, every year 2 million people die from diabetes and its complications around the world. In the absence of qualified support for the body, diabetes leads to various kinds of complications, gradually destroying the human body.
The most common complications are: diabetic gangrene, nephropathy, retinopathy, trophic ulcers, hypoglycemia, ketoacidosis. Diabetes can also lead to the development of cancer. In almost all cases, a diabetic either dies fighting a painful disease or becomes a real disabled person.
What should people with diabetes do? The Endocrinological Research Center of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences succeeded make a remedy completely cures diabetes mellitus.
Currently, the Federal program “Healthy Nation” is underway, within the framework of which this drug is given to every resident of the Russian Federation and the CIS FOR FREE. For detailed information, see official website MINISTRY OF HEALTH.
- Primary rashes - here doctors include local dermatosis and other skin pathologies caused by a disruption of the normal metabolic process.
- Group of secondary pathologies. In this case, such rashes are provoked by an infection. Fungi and bacteria, other pathogenic microorganisms can affect the dermis, thereby causing itching and burning, redness and spots.
- Skin damage in diabetes mellitus as a result of taking medications aimed at normalizing blood glucose levels.
The prognosis for the treatment of dermatosis caused by diabetes mellitus directly depends on how quickly and correctly it is possible to correct the patient’s condition for the better, restoring the natural metabolic processes in his body.
Primary group

Doctors include diseases that affect the dermis in this group.
- Diabetic type of dermopathy - marked by changes in the network of small blood vessels. In this case, a characteristic symptom is spots on the skin due to diabetes mellitus, peeling and itching at the site of the lesion. So spots, peeling and itching of the skin with diabetes do not require treatment.
- Lipoid type of necrobiosis - this symptom is most often the very first to indicate elevated blood sugar levels. Most often it is diagnosed in women, less often in men and shows itself in the form of large spots affecting the scalp and face, colored in a bluish, bright color. In addition to spots on the body, nodular neoplasms can also form over time, marked in the center by atrophic processes and ulcerations.
- The peripheral form of atherosclerosis is a lesion of the vascular network characteristic of diabetes, most often affecting the legs and accompanied by the formation of atherosclerotic plaques, leading to blockage of blood vessels. This is how the skin in diabetes becomes covered with a network of spider veins, with veins protruding onto the surface. It becomes too dry and begins to peel. Even the slightest wound or scratch may not heal for a long time, and the patient is bothered by pain when walking or standing still.
- Xanthomatosis eruptive - shows itself as small yellow rashes, similar to a small rash, the elements of which are covered with red rims along the edge. Most often, such rashes cover the patient’s back, inner thigh and buttocks and are more often diagnosed in diabetics with high levels of bad cholesterol in the blood.
- Granuloma annulare is a rash that has the shape of an arc or a ring, and is mostly localized on the wrist and toes, and the inside of the foot.
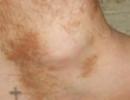
- Papillary pigment dystrophy developing in the patient. Most often, such skin damage in type 2 diabetes is localized in the armpits and neck, in the groin and on the inside of the thigh, where skin folds form. A characteristic manifestation is the appearance of brown spots on the body and is most often found in patients with cellulite and excess weight.
- Itchy forms of dermatoses are also harbingers of the appearance of elevated blood sugar levels in the patient. There is no precise confirmation of the direct relationship between the severity of itching and redness, peeling and dryness of the dermis, and the degree of development of diabetes mellitus. As an example, during diabetes in its hidden, latent form, the patient may experience severe itching.
Secondary group

With the development of diabetes, the patient's skin is often affected by fungi and other fungal dermatoses, in particular candidiasis. Most often, the symptoms of the disease manifest themselves as severe itching and the appearance of a whitish coating on the mucous membranes and in the folds of the skin.
Our readers write
Subject: Conquered diabetes
From: Lyudmila S ( [email protected])
To: Administration my-diabet.ru

At the age of 47, I was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. In a few weeks I gained almost 15 kg. Constant fatigue, drowsiness, feeling of weakness, vision began to fade. When I turned 66, I was already steadily injecting myself with insulin, everything was very bad...
And here is my story
The disease continued to develop, periodic attacks began, and the ambulance literally brought me back from the other world. I always thought that this time would be the last...
Everything changed when my daughter gave me an article to read on the Internet. You can’t imagine how grateful I am to her for this. This article helped me completely get rid of diabetes, a supposedly incurable disease. Over the last 2 years I have started to move more, in the spring and summer I go to the dacha every day, my husband and I lead an active lifestyle and travel a lot. Everyone is surprised how I manage to do everything, where so much strength and energy comes from, they still can’t believe that I’m 66 years old.
Who wants to live a long, energetic life and forget about this terrible disease forever, take 5 minutes and read this article.
Go to article>>>
If treatment measures are not taken in a timely manner, cracks, ulcers and other lesions may appear on the skin and mucous membranes.
Infections that have a bacterial form of origin with elevated blood sugar levels show themselves in the form of erysipelas and carbuncles, purulent abscesses and phlegmons.
Most often, the cause of such rashes is streptococcal or staphylococcal pathogenic microflora.
Dermatoses provoked by taking medications are also common. This group of pathological changes in the skin is also quite common. Skin lesions in this case are a consequence of constant use of medications that control blood sugar levels and an allergic response of the body.
Drawing conclusions
If you are reading these lines, we can conclude that you or your loved ones have diabetes.
We conducted an investigation, studied a bunch of materials and, most importantly, tested most of the methods and medications for diabetes. The verdict is:
If all drugs were given, it was only a temporary result; as soon as the use was stopped, the disease sharply intensified.
The only drug that has given significant results is Difort.
At the moment, this is the only drug that can completely cure diabetes. Difort showed a particularly strong effect in the early stages of the development of diabetes mellitus.
In this article we will talk about diabetes mellitus symptoms photo, study the signs of diabetes mellitus, find out what ulcers and spots on the legs look like with diabetes mellitus photo, and also see a rash with diabetes mellitus photo.
The symptoms of diabetes are varied; every twentieth person suffers from it. A large number of people have hidden diabetes or a genetic predisposition to it. Therefore, it is important to have a good understanding of the signs of diabetes in order to consult a doctor for help in time.
Clinical picture
What doctors say about diabetes
Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Aronova S. M.

I have been studying the problem of DIABETES for many years. It's scary when so many people die and even more become disabled due to diabetes.
I hasten to report good news - the Endocrinological Research Center of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences managed to develop a medicine that completely cures diabetes mellitus. At the moment, the effectiveness of this drug is approaching 100%.
Another good news: the Ministry of Health has achieved the adoption special program, which reimburses the entire cost of the drug. In Russia and the CIS countries, diabetics to can get the remedy FOR FREE.
Find out more>>
Diabetes mellitus: signs and symptoms
An early sign of the disease can be a deterioration in the healing process of even minor wounds. Boils and acne with diabetes(photo 2) are also early signs of trouble with the pancreas.
Itchy skin in diabetes mellitus (photo below) is observed in 80% of cases.
Diabetes mellitus is indicated by increased pigmentation of skin folds and the appearance of small warts around them (acanthosis).
And such skin rashes in diabetes mellitus (photo in gal), such as diabetic pemphigus, indicate deep skin damage and require surgical intervention.
Spots on legs due to diabetes
Dermatoses - spots on the legs with diabetes mellitus (pictured 3) - are most often located on the lower leg, but there are other favorite locations. White round spots in diabetes mellitus - vitiligo– serve as a signal of the development of the disease. Yellow lumps – xanthomatosis – indicate increased blood sugar.
Be careful
According to WHO, every year 2 million people die from diabetes and its complications around the world. In the absence of qualified support for the body, diabetes leads to various kinds of complications, gradually destroying the human body.
The most common complications are: diabetic gangrene, nephropathy, retinopathy, trophic ulcers, hypoglycemia, ketoacidosis. Diabetes can also lead to the development of cancer. In almost all cases, a diabetic either dies fighting a painful disease or becomes a real disabled person.
What should people with diabetes do? The Endocrinological Research Center of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences succeeded make a remedy completely cures diabetes mellitus.
Currently, the Federal program “Healthy Nation” is underway, within the framework of which this drug is given to every resident of the Russian Federation and the CIS FOR FREE. For detailed information, see official website MINISTRY OF HEALTH.
Diabetes mellitus rashes (photo in the gallery) can also appear in the form of large bluish-red spots of irregular shape, prone to enlargement. Such signs of diabetes in women are much more common than in men. This is the so-called necrobiosis lipoidica.
Gradually, the skin on the lower legs becomes thin, rough and dry. When degenerative processes intensify, ulcers appear on the legs due to diabetes mellitus (pictured 4). This process is facilitated by a decrease in sensitivity - minor abrasions and sores on the legs with diabetes (photo in gal) do not alarm a person.
Main causes ulcers in diabetes mellitus– these are previous bruises, calluses and microtraumas. But the true factors that cause leg ulcers in diabetes mellitus, of course, lie much deeper in the disruption of blood supply and innervation of the lower extremities. The ulcers become infected and spread along the surface of the leg.
Our readers write
Subject: Conquered diabetes
From: Lyudmila S ( [email protected])
To: Administration my-diabet.ru

At the age of 47, I was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. In a few weeks I gained almost 15 kg. Constant fatigue, drowsiness, feeling of weakness, vision began to fade. When I turned 66, I was already steadily injecting myself with insulin, everything was very bad...
And here is my story
The disease continued to develop, periodic attacks began, and the ambulance literally brought me back from the other world. I always thought that this time would be the last...
Everything changed when my daughter gave me an article to read on the Internet. You can’t imagine how grateful I am to her for this. This article helped me completely get rid of diabetes, a supposedly incurable disease. Over the last 2 years I have started to move more, in the spring and summer I go to the dacha every day, my husband and I lead an active lifestyle and travel a lot. Everyone is surprised how I manage to do everything, where so much strength and energy comes from, they still can’t believe that I’m 66 years old.
Who wants to live a long, energetic life and forget about this terrible disease forever, take 5 minutes and read this article.
Go to article>>>
Diabetes rash
Skin rashes in diabetes mellitus (photo 5) take on a variety of appearances. Due to metabolic disorders, round, painless red-brown nodules 5-12 mm in diameter appear on the skin of the lower leg.
Acne diabetes rash(pictured below) occurs due to the body’s desire to remove excess glucose through the sweat glands of the skin. Reduced immunity contributes to the attachment of bacterial flora - pustules form. Diabetes rash occurs in 30-35% of patients.
Diabetes usually causes complications on the legs. Blood circulation in them is disrupted, this leads to serious consequences. Feet for diabetes(in photo 5) gradually lose sensitivity to temperature, pain and tactile stimuli.
The foot with diabetes mellitus (photo below) suffers due to congestion in the venous system, often sending pain signals when walking, and sometimes at rest. But another condition is more dangerous - when a limb, due to the destruction of nerve endings, loses sensitivity and trophic ulcers develop on it. Redness of the foot in diabetes in the form of spots indicates the development of diabetic foot. This is a late stage of the disease.
Stories from our readers
Conquered diabetes at home. It's been a month since I forgot about sugar spikes and taking insulin. Oh, how I used to suffer, constant fainting, calls to the ambulance... How many times have I gone to endocrinologists, but they only say one thing - “Take insulin.” And now it’s been 5 weeks and my blood sugar levels are normal, not a single injection of insulin, and all thanks to this article. A must read for anyone with diabetes!
Read the full article >>>Nails for diabetes
Symptoms of diabetes mellitus also manifest themselves in the form of deformation of fingers and nails. Toes with diabetes mellitus (photo below) become thicker, deformed, and red or bluish spots appear on them.
They have a characteristic appearance nails for diabetes(pictured 6): they become brittle, flake, and often grow into the skin at their corners. Often an associated fungal infection is to blame. Fragility of capillaries, especially with tight shoes, leads to hemorrhages under the nail plate, and the nails turn black.
Gangrene in diabetes mellitus
Studying the question what is diabetes mellitus, one cannot ignore its most serious complication - gangrene in diabetes mellitus (in photo 7), which creates a danger to the patient’s life. Non-healing wounds on the legs with diabetes mellitus can exist for several years. Their outcome is either wet or dry. gangrene of the lower extremities(photo below). With diabetes mellitus, this happens, alas, often when the disease lasts for many years. Gangrene in diabetes mellitus requires surgical intervention.
Having familiarized yourself in detail with what diabetes mellitus looks like (photo in gal) at all stages, it is easier to assess the danger of its individual symptoms. Having identified signs of diabetes, you should immediately contact a specialist for help. This will make it possible to prevent serious consequences. Diabetes mellitus does not forgive delays in treatment.
Diabetes mellitus pictures and photos (gallery)
Drawing conclusions
If you are reading these lines, we can conclude that you or your loved ones have diabetes.
We conducted an investigation, studied a bunch of materials and, most importantly, tested most of the methods and medications for diabetes. The verdict is:
If all drugs were given, it was only a temporary result; as soon as the use was stopped, the disease sharply intensified.
The only drug that has given significant results is Difort.
At the moment, this is the only drug that can completely cure diabetes. Difort showed a particularly strong effect in the early stages of the development of diabetes mellitus.
We made a request to the Ministry of Health:
And for readers of our site there is now an opportunity
receive Difort FOR FREE!
Attention! Cases of sales of counterfeit drug Difort have become more frequent.
By placing an order using the links above, you are guaranteed to receive a quality product from the official manufacturer. In addition, when ordering from official website, you receive a money-back guarantee (including transportation costs) if the drug does not have a therapeutic effect.
Impaired glucose metabolism in diabetic patients leads to the appearance of pathological changes in all organs of the human body, without exception. The cause of skin pathology in diabetes mellitus is a high concentration of sugar and the accumulation of toxic products of distorted metabolism. This leads to structural changes not only in the dermis and epidermis, but also in the sebaceous, sweat glands and hair follicles.
Diabetics also experience diabetic polyneuropathy and microangiopathy, which also negatively affect the skin. All these factors, as well as a decrease in general and local immunity, lead to the occurrence of wounds, ulcers and purulent-septic processes.
Skin changes
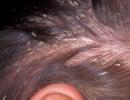
Due to the disease, the skin of diabetics becomes very dry, rough to the touch, and its turgor decreases. Hair becomes dull and falls out more often than usual, since the hair follicle is very sensitive to metabolic disorders. But diffuse baldness indicates poorly controlled diabetes or the development of complications. For example, hair loss on the lower legs in men may indicate neuropathy of the lower extremities.
The soles and palms become covered with cracks and calluses. Often the skin acquires an unhealthy yellowish tint. The nails thicken, become deformed, and hyperkeratosis of the subungual plate develops.
Often, dermatological symptoms, such as dry and itchy skin and mucous membranes, recurrent skin fungal and bacterial infections, act as a signal about the onset of diabetes.
Classification of skin lesions in diabetes
Modern medicine has described about 30 different dermatoses that develop against the background of this disease or precede it.

All skin pathologies in diabetics can be divided into 3 large groups:
- Primary – skin lesions that are caused by the direct effects of diabetes complications. Namely, diabetic neuro- and angiopathy and metabolic disorders. Primary pathologies include diabetic xanthomatosis, diabetic dermatopathies, necrobiosis lipoidica, diabetic blisters, etc.;
- Secondary are skin diseases caused by bacterial and fungal infections, frequent relapses of which occur due to diabetes mellitus;
- Dermatoses caused by drugs used in the treatment of diabetes. These include post-injection lipodystrophy, toxicerma, urticaria, and eczematous reactions.
Diabetic skin lesions, as a rule, last a long time and are characterized by frequent exacerbations. They are difficult to treat.
Diabetic dermatopathy
The most common skin lesion in diabetes mellitus. Angiopathy develops, that is, changes in microcirculation in the blood vessels that supply the skin with blood.
Dermopathy is manifested by the appearance of reddish-brown papules (5–12 mm in diameter) on the anterior surface of the legs. Over time, they merge into oval or round atrophic spots, followed by thinning of the skin. Such skin lesions are detected more often in men with a long history of diabetes mellitus.
Symptoms, as a rule, are absent, there is no pain, but sometimes patients experience itching or burning in the affected areas. There are no methods for treating dermopathy; it may go away on its own in a year or two.
Necrobiosis lipoidica
Chronic dermatosis, which is characterized by fatty degeneration and focal disorganization of collagen. The cause of this disease is insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Mostly women aged 15 to 40 years are affected, but necrobiosis lipoidica can develop in any diabetic.
There is no direct relationship between the severity of the clinical manifestations of this dermatosis and the severity of diabetes.
The cause of this diabetic skin lesion is microangiopathy and secondary necrobiotic changes. If they are present, necrosis of elastic fibers and inflammation with migration of inflammatory agents into the focus of necrosis are observed. An important role in the pathogenesis of necrobiosis is played by increased platelet aggregation, which, together with endothelial proliferation, leads to thrombosis of small vessels.

Necrobiosis lipoidica begins with the appearance on the skin of the lower leg of small single bluish-pink spots or flat, smooth nodules of oval or irregular shape. These elements tend to grow along the periphery with the further formation of elongated, clearly demarcated polycyclic or oval indurative-atrophic plaques. The yellowish-brown central part is slightly sunken, and the bluish-red marginal part is slightly raised. The surface of the plaques is smooth, rarely peeling off at the periphery.
Over time, the central part of the plaques atrophies, spider veins (telangiectasia), mild hyperpigmentation, and in some cases areas of ulceration appear on it. In most cases, there are no subjective sensations. During the period when ulcers appear, pain occurs.
The picture of skin lesions in necrobiosis lipoidica is so typical that there is generally no need for additional research. Differential diagnosis is carried out only for atypical forms with sarcoidosis, granuloma annulare, xanthomatosis.
Scientists believe that in 1/5 of diabetics, necrobiosis lipoidica may appear 1-10 years before the development of specific diabetes symptoms.
Treatment of necrobiosis lipoidica
There is no effective treatment for necrobiosis lipoidica. Drugs are recommended that normalize lipid metabolism and improve microcirculation. Vitamins and multivitamin complexes are also prescribed. Intralesional injections of heparin, insulin, and corticosteroids are successfully used.
Externally shown:
- applications with dimexide solution (25–30%);
- troxevasin, heparin ointments;
- dressings with corticosteroid ointments.
Physiotherapy. Phono - or electrophoresis with hydrocortisone, aevit, trental. Laser therapy, rarely ulcerations are removed surgically.
Pruritic dermatoses
This pathology is also called neurodermatitis, and it manifests itself as itchy skin. Very often, neurodermatitis becomes the first symptom of diabetes. Localization is predominantly in the folds of the abdomen, limbs, and genital area.
There is no direct relationship between the intensity of itching and the severity of diabetes. However, it has been noted that the most persistent and severe itching is observed in “silent” (hidden) and mild diabetes mellitus. Neurodermatitis can also develop due to poor blood sugar control in established diabetes.
Fungal skin diseases in diabetics
The most common cause of candidiasis is Candida albicans. Recurrent candidiasis is one of the first symptoms of the development of diabetes mellitus.
It occurs mainly in elderly and obese patients. It is localized mainly in the genital area and large folds of skin, as well as on the mucous membranes, in the interdigital folds. With any localization of candidiasis, its first sign is persistent and severe itching, which is then accompanied by other objective symptoms of the disease.
Initially, a whitish strip of macerated epidermis appears in the depths of the fold, and surface erosions and cracks form. The erosions have a shiny and moist surface; the defect itself is bluish-red and is limited by a white rim. The main focus of candidiasis is surrounded by small superficial pustules and vesicles, which are its screenings. These elements of the rash open up and become erosions, thus the area of the erosive surface increases. The diagnosis can be easily confirmed by culture and microscopic examination.
Treatment of candidiasis in diabetes
Therapy should be comprehensive and include:
- antifungal ointments or creams that need to be applied until the rash disappears, and then for another 7 days;
- solutions of aniline dyes, they can be alcoholic or aqueous (for a large affected area). These include - 1% solution of brilliant green, 2-3% solution of methylene blue. Castellani liquid and 10% boric acid ointment are also used for local treatment;
- systemic antifungal agents fluconazole, ketoconazole, itraconazole. The common sense of prescribing these drugs is that they are quite effective, affordable, and thanks to them you can quickly get rid of the symptoms of candidiasis.
Bacterial skin diseases in diabetics
The most common skin ailments in diabetes mellitus. The difficulty is that they are difficult to treat and lead to life-threatening complications such as sepsis or gangrene. Infected diabetic foot ulcers can lead to leg amputation or death if not treated promptly.
Diabetics are much more likely than the rest of the population to have boils, carbuncles, pyoderma, cellulitis, erysipelas, paronychia and panaritium. As a rule, they are caused by streptococci and staphylococci. The addition of infectious and inflammatory skin diseases leads to long-term and severe exacerbations of diabetes and requires the prescription or increase in the dose of insulin.
Therapy for these diseases should be based on the results of a study of the type of pathogen and its sensitivity to antibiotics. The patient is prescribed tablet forms of broad-spectrum antibiotics. If necessary, surgical procedures are performed, for example, opening a boil, draining an abscess, etc.

Diabetic dermatoses such as diabetic bullae, rubeosis, acanthokeratoderma, diabetic scleroderma, diabetic xanthoma, and disseminated granuloma annulare are very rare.
Skin lesions in diabetics are quite common today. Treatment of these conditions involves certain difficulties. It should begin with successful control of blood sugar concentrations and selection of an adequate set of medications for diabetes. Without correction of carbohydrate metabolism in this group of patients, all treatment methods are ineffective.